# vue-cheat-sheet
My cheat sheet for vue.js most basic stuff. The goal wasn't to make another Vue documentation, because the official one is already badass.
Contributions and PRs are very welcome.
"You must type each of these exercises in, manually. If you copy and paste, you might as well not even do them. The point of these exercises is to train your hands, your brain, and your mind in how to read, write, and see code. If you copy-paste, you are cheating yourself out of the effectiveness of the lessons." - Zed A.
Sources:
Useful Chrome extensions:
Stuff that might get handy in almost every Vue.js project:
# Basic HTML and JS
<template>
<div id="vue-app">
<p>{{ hello() }}</p>
<p>{{ name }}</p>
<p>{{ age + 1 }}</p>
<p>{{ age < 18 ? "Youngster" : "Adult"}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
name: "Matej",
age: 27,
sleepy: true
};
},
methods: {
hello: function() {
return "Hello";
}
}
};
</script>
<style>
</style>
Hello
Matej
28
Adult
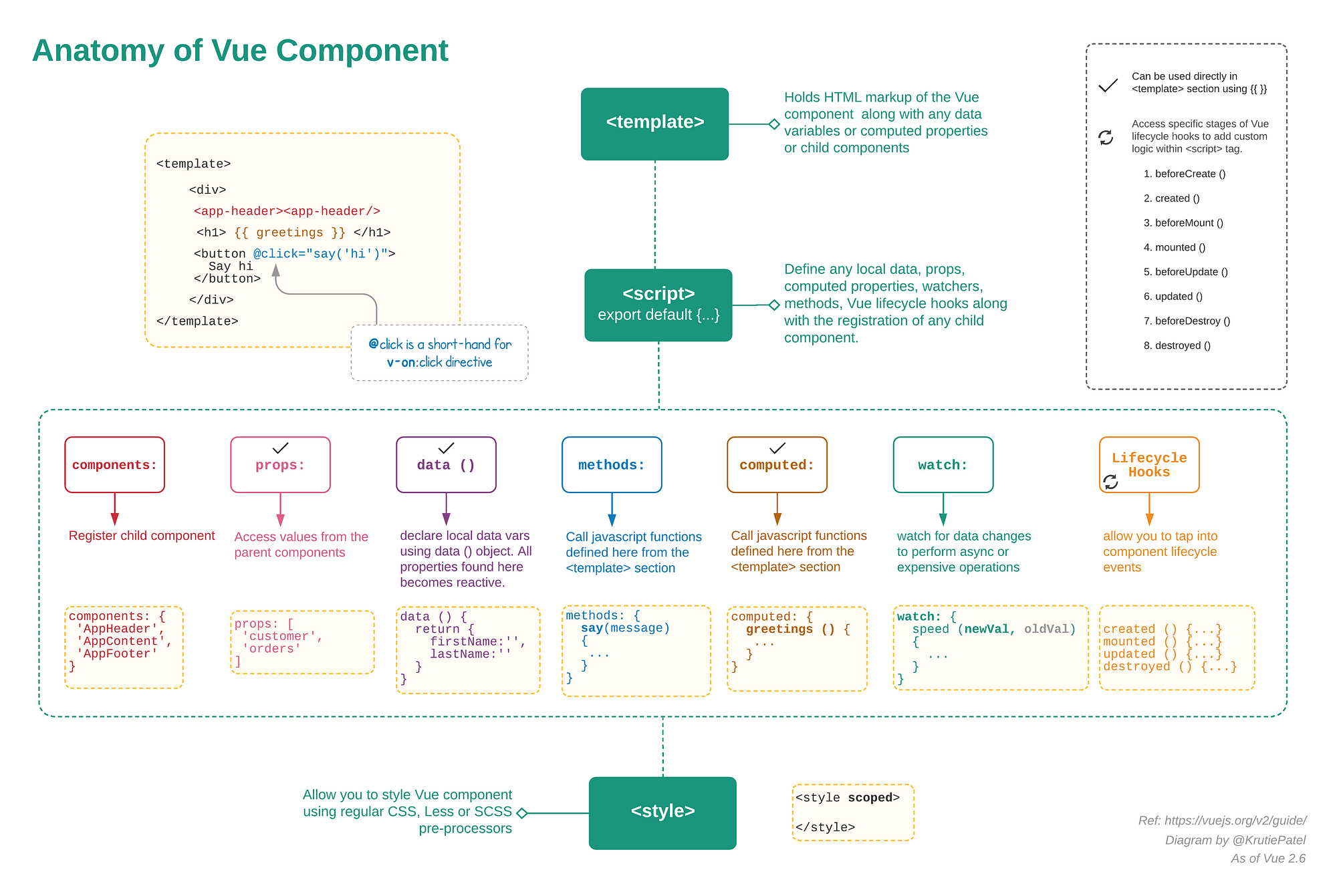
# Anatomy of Vue component
# HTML directives
# Show / hide div
# Hides the element (display none), doesn't delete it
where available is a boolean variable in the js script
<div v-show="available">Stuff</div>
<template>
<div>
<button class="btn" v-on:click="toggle=!toggle">
Toggle
</button>
<h4 v-show="toggle">Content rendered conditionally</h4>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
toggle:false
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
.btn{
padding: 6px 16px;
font-size: 0.875rem;
min-width: 64px;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-weight: 500;
line-height: 1.75;
border-radius: 4px;
letter-spacing: 0.02857em;
text-transform: uppercase;
outline: none;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
Content rendered conditionally
# Conditional rendering
it deletes the element from the DOM tree
<div v-if="available">Stuff</div>
<div v-else>Smth else</div>
<template>
<div>
<button class="btn" v-on:click="toggle=!toggle">
Toggle
</button>
<h4 v-if="toggle">Content rendered conditionally</h4>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
toggle:false
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
.btn{
padding: 6px 16px;
font-size: 0.875rem;
min-width: 64px;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-weight: 500;
line-height: 1.75;
border-radius: 4px;
letter-spacing: 0.02857em;
text-transform: uppercase;
outline: none;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
# Looping
# array of strings
Remember to check if the element exists with v-if before looping over it
<ul>
<li v-for="(element, index) in elements">{{index}} {{element}}</li>
</ul>
# array of objects
WARNING
Don't use v-if and v-for in the same element for more details check this article
<ul v-if="employee">
<li v-for="employee in employees">{{employee.name}} - {{employee.age}}</li>
</ul>
# nested arrays
<table>
<tr>
<th>Amount</th>
<th>Asset</th>
<th>Created</th>
</tr>
<template v-for="u in users">
<tr v-for="t in u.transfers">>
<td>{{ t.amount }}</td>
<td>{{ t.asset }}</td>
<td>{{ t.timestamp }}</td>>
</tr>
</template>
</table>
# variables in v-for
<li v-for="id in users" :key="id" :set="item = getUserData(id)">
<img :src="item.avatar" /><br />
{{ item.name }}<br />
{{ item.homepage }}
</li>
<template>
<div>
<h5>Foos :</h5>
<ul>
<li v-for="(bar,index) in bars" :key="bar">{{bar}} - {{index}}</li>
</ul>
<h5>user details</h5>
<ul>
<li v-for="(val,key, index) in user" :key="index">{{key}} : {{val}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
bars: ["foo", "bar", "test"],
user: {
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe",
age: 28,
email: "john_doe@gmail.com"
}
};
},
methods: {}
};
</script>
<style>
</style>
Foos :
- foo - 0
- bar - 1
- test - 2
user details
- firstName : John
- lastName : Doe
- age : 28
- email : john_doe@gmail.com
Set html for element from a variable name
<span v-html="name"></span>
The v-html directive outputs the real html rendered content not a plain text
<template>
<div v-html="html"></div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
html:'<h3>Hello there !</h3>'
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
Hello there !
# Two way data binding
v-model directive allows you to bind a data object property with a form input :
<input v-model="name" type="text" />
<p>My name is: {{name}}</p>
...
data(){
return{
name: ""
}
}
...
My name is:
# Computed properties
Computed properties are cached, and only re-computed on reactive dependency changes. Note that if a certain dependency is out of the instance’s scope (i.e. not reactive), the computed property will not be updated. In other words, imagine a computed property as a method (but it's not really a method) in the
data()that always returns a value. That "method" will be called whenever a property (variable fromdata()) used in that method is changed.
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf8">
<title>VueJS example</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="vue-app">
<button v-on:click="a++">Counter 1++</button>
<button v-on:click="a--">Counter 1--</button>
<button v-on:click="b++">Counter 2++</button>
<p>Counter 1: {{ a }}</p>
<p>Counter 2: {{ b }}</p>
<!--The result() method is invoked whenever the Counter 1 button is clicker or the Counter 2 button is clicked-->
<!--The output() method is invoked only when the Counter 2 button is clicked-->
<p>Result: {{ result() }} | {{ output }}</p>
</div>
<script src="main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
new Vue({
el: '#vue-app',
data: {
a: 0,
b: 0
},
methods: {
result: function () {
// this function is not interested in the "b" variable, yet it runs every time when the result needs to be changed
console.log("methods");
return this.a < 0 ? "Negative" : "Positive";
}
},
computed: {
// these methods are invoked like attributes, without ()
// this method runs only when the "a" variable is changed
output: function () {
console.log("computed");
return this.a < 0 ? "Negative" : "Positive";
}
}
});
# Computed property methods can also have getters and setters
var vm = new Vue({
data: { a: 1 },
computed: {
// get only
aDouble: function () {
return this.a * 2
},
// both get and set
aPlus: {
get: function () {
return this.a + 1
},
set: function (v) {
this.a = v - 1
}
}
}
})
vm.aPlus // => 2
vm.aPlus = 3
vm.a // => 2
vm.aDouble // => 4
# HTML properties and classes
<p v-bind:style="{ property: value }">...</p>
this div will have the red class if the userFound variable is set to true
<div v-bind:class="{ red: userFound }">...</div>
this div will have the red class if the isAdmin variable is set to true
<div :class="[isAdmin ? 'red' : 'blue']">...</div>
# Events
# Call method on click event
where method is a custom method in the js
<button v-on:click="method">Add</button>
# or shorthand
where method is a custom method in the js
<button @click="method">Add</button>
method is called when ALT+ENTER is pressed
<input ref="name" v-on:keyup.alt.enter="method" type="text" />
<template>
<div>
<p>Focus on this input and press alt+enter</p>
<input v-on:keyup.alt.enter="method1" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
method1(){
alert('This event is fired when you press alt+enter !')
console.log('This event is fired when you press alt+enter !')
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
Focus on this input and press alt+enter
# Conditional event binding (as of Vue 2.6)
The method sendModey will be called only if the condition amount > 0 has been met.
<button @click="amount > 0 && sendMoney()">Send money</button>
# Custom events
// fire custom event
this.$emit("eventName", data);
<!--
$event == event data
when _eventName_ event happens, call _functionName_ function
-->
<p v-on:eventName="functionName($event)"></p>
# Event bus
# communicate between child components without the parent component
# consider using Vuex instead
// main.js
// create new event bus
export const bus = new Vue();
// Header.vue
import {bus} from "../main";
// Footer.vue
import {bus} from "../main";
// listen to bus event in first component
// usually in .created() function
bus.$on("eventName", (data) => {
// callback
// use data
})
// fire bus event in second component
bus.$emit("eventName", data);
# Components
# reusable inside the html
<div id="app">
<!-- <component is="signature"></component> -->
<signature></signature>
<signature></signature>
</div>
// global registration
Vue.component('signature', {
template: '<p>Regards. Matej.</p>'
});
# .vue components and props
# Props - passing data from parent component to child component
<!--App.vue-->
<template>
<div>
<app-header></app-header>
<app-ninjas v-bind:ninjas="ninjas"></app-ninjas>
<app-footer></app-footer>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import
import Header from './components/Header.vue';
import Footer from './components/Footer.vue';
import Ninjas from './components/Ninjas.vue';
export default {
// register components
components:{
// added app- prefix
// because header and footer tags already exist
"app-header": Header,
"app-footer": Footer,
"app-ninjas": Ninjas
},
data () {
return {
ninjas:[
{name: "ninja1", speciality: "vuejs", show: false},
{name: "ninja2", speciality: "nodejs", show: false},
{name: "ninja3", speciality: "react", show: false},
{name: "ninja4", speciality: "js", show: false},
{name: "ninja5", speciality: "css3", show: false},
{name: "ninja6", speciality: "ps", show: false}
]
}
}
}
</script>
<!--Ninjas.vue-->
<template>
<div id="ninjas">
<ul>
<li v-for="ninja in ninjas" v-on:click="ninja.show = !ninja.show">
<h2>{{ninja.name}}</h2>
<h3 v-show="ninja.show">{{ninja.speciality}}</h3>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// what is it receiving
props: ["ninjas"],
data: function () {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
<!--Header.vue-->
<template>
<header>
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
</header>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function () {
return {
title: "Welcome!"
}
}
}
</script>
<!--Footer.vue-->
<template>
<footer>
<p>{{copyright}}</p>
</footer>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function () {
return {
copyright: "Copyright 2017 "
}
}
}
</script>
# Validate props
export default {
props:{
ninjas:{
type: Array,
required: true
}
}
}
# Filters
# Change the output data to the browser. They do not change the data directly.
<h1>{{title | to-uppercase}}</h1>
// main.js
Vue.filter("to-uppercase", function ( value ) {
return value.toUpperCase();
});
# Mixins
# Reuse some piece if code (or function) so that it doesn't need to be written in more separate files.
# References
# An object of DOM elements and component instances
<input ref="name" type="text" />
var name = this.$refs.name;
# Dynamic components
dynamically change component based on variable component value rememberto use keep-alive tag to remember data from the destroyed component
<template>
<div>
<component> v-bind:is="componentName"></component>
</div>
</template>
import formOne from "./components/formOne.vue";
import formTwo from "./components/formTwo.vue";
...
data: function() {
return {
component: "form-two"
}
}
# Vue CLI
# make new project
$ vue init webpack-simple my-project
$ cd project-name
# install dependencies and start local server
$ npm install
$ npm run dev
# build app for production
this will make a dist folder with minified js
$ npm run build
# Vue CLI 3
# make new project
$ vue create my-project
$ cd project-name
# install dependencies and start local server
$ npm install
$ npm run serve
# build app for production
this will make a dist folder with minified js
$ npm run build
# Vue lifecycle
- new Vue();
- .beforeCreate();
- .created();
- .beforeMount();
- .updated();
- .beforeUpdate();
- .beforeDestroy();
- .destroyed();

# Checkboxes
# with v-model, the categories array will be appended with the values
<div>
<label for="">Newsletters</label>
<input type="checkbox" value="newsletter" v-model="categories">
<label for="">New posts</label>
<input type="checkbox" value="post" v-model="categories">
<label for="">New DMs</label>
<input type="checkbox" value="dm" v-model="categories">
<label for="">New pokes</label>
<input type="checkbox" value="pokes" v-model="categories">
</div>
data: function () {
categories: []
}
# Select box binding
# hardcoded and looped select
<div>
<select v-model="town">
<option value="osijek">Osijek</option>
<option value="zagreb">Zagreb</option>
<option value="varazdin">Varazdin</option>
</select>
<select v-model="town">
<option v-for="t in towns">{{ t }}</option>
</select>
</div>
data: function () {
town: "",
towns: ["Zagreb", "Algiers","Aflou","Aleppo","Osijek", "Varazdin", "Split", "Rijeka", "Dubrovnik",]
}
# Vue resource
# POST requests with vue-resource
Important: if sending nested objects, be sure to JSON.stringify first!
# Register it in main.js
import VueResource from 'vue-resource'
Vue.use(VueResource);
# Usage in custom function
post: function () {
this.$http.post("http://localhost:3000/users", {
title: this.blog.title,
body: this.blog.body,
userId: 1
}).then( res => {
// promise
console.log("Response: ", res);
}, error => {
console.log("Error: ", error);
});
}
# GET requests
# Usage in custom function
post: function () {
this.$http.get("http://localhost:3000/users").then( function ( res ){
// promise
console.log("Response: ", res)
});
}
# Vue with axios
# installation
npm install axios vue-axios --save
# Registration in app.js or main.js
import axios from 'axios';
import VueAxios from 'vue-axios';
Vue.use(VueAxios, axios);
then you could get access to this.axios in any child component :
this.axios.get(URL).then((result) => {
//handle the result in case if the request is successfully processed
}).catch((err) => {
//handle the error
});
...
this.axios.post(URL,{
//request body
}).then((result) => {
//handle the result in case if the request is successfully processed
}).catch((err) => {
//handle the error
});
# Routes with vue-router
// router.js
import login from "./components/login.vue";
import registration from "./components/Registration.vue";
import user from "./components/user.vue";
// main.js
import VueRouter from 'vue-router';
import { routes } from "./routes";
Vue.use(VueRouter);
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
});
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router: router,
render: h => h(App)
})
// routes.js
import Login from "./components/Login.vue";
import Registration from "./components/Registration.vue";
import User from "./components/User.vue";
export const routes = [
{ path: "", component: Login },
{ path: "/registration", component: Registration },
{ path: "/users/", component: Users, children: [
{ path: "", component: UserStart },
{ path: ":id", component: UserDetail },
{ path: ":id/edit", component: UserEdit }
] },
{path: "*", redirect: "/"} // handle all uncovered routes
]
# mark the place with router-view where the component of the currently active route will be loaded
<template>
<router-view></router-view>
</template>
# handling route parameters
<!-- user.vue -->
<template>
<div id="user">
<h1></h1>
<div></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function () {
return {
id: this.$route.params.id,
user: {}
}
},
created(){
this.$http.get("http://url/user/" + this.id).then(function(res){
this.user = res.body;
});
}
}
</script>
# navigating around
<ul class="nav">
<router-link to="/" tag="li" active-class="active" exact><a>Home</a></router-link>
<router-link to="/users" tag="li" active-class="active" ><a>Users</a></router-link>
</ul>
# dynamically route over user details
<router-link v-bind:to='"/user/" + user.id' tag="li" v-for="(user, index) in users"> {{ user.username }}</router-link>
# navigate home
this.$router.push({ path: "/home"});
# watch for route changes
watch: {
"$route": function (to, form){
this.id = to.params.id
}
}
# watch if object is changed
watch: {
picked: {
handler(val, oldVal) {
console.log('changed: ', oldVal);
console.log('new: ', val);
},
deep: true,
immediate: true
}
}
# auth restrictions
To not let someone access e.g. /dashboard if the user is not logged in.
// add requiresAuth to certain components
export const routes = [
{ path: "", component: Login },
{ path: "/dashboard", component: Dashboard, meta: {requiresAuth: true} }
];
// configure vue-router
// important: do not turn on history mode
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
// mode: "history"
})
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (to.matched.some(record => record.meta.requiresAuth)) {
if ( CHECK_FOR_USER_IN_LOCALSTORAGE_ETC ) {
// handle restricted access
next({
path: '/login',
});
} else {
next();
}
} else {
// do nothing with components without meta: {requiresAuth: true}
next();
}
})
# table search + sort
# multiple column search
<!--input field for search query-->
<input type="text" v-model="searchQuery" placeholder="Search...">
<!--loop like this, instead of classic for user in users-->
<tr v-for="user in filterUsers">
// users array and search query variable
data: function () {
return {
searchQuery: "",
users: []
};
},
...
// computed method for filtering users by
// email, last name and first name
computed: {
filterUsers () {
return this.users.filter(user => {
return (user.email.toLowerCase().indexOf(this.searchQuery.toLowerCase()) > -1 ||
user.lastName.toLowerCase().indexOf(this.searchQuery.toLowerCase()) > -1 ||
user.firstName.toLowerCase().indexOf(this.searchQuery.toLowerCase()) > -1)
})
}
}
# sort columns asc and desc
// add needed variables
data: function () {
return {
ascending: false,
sortColumn: '',
users: [],
};
},
methods: {
// sort method
"sortTable": function sortTable ( col ) {
if ( this.sortColumn === col ) {
this.ascending = !this.ascending;
} else {
this.ascending = true;
this.sortColumn = col;
}
let ascending = this.ascending;
this.users.sort(function ( a, b ) {
if ( a[col] >= b[col] ) {
return ascending ? 1 : -1
} else if ( a[col] < b[col] ) {
return ascending ? -1 : 1
}
return 0;
})
}
}
<!--call sortTable method on column with corresponding property in users object-->
<tr>
<th @click="sortTable('email')">Username</th>
<th @click="sortTable('firstName')">First Name</th>
<th @click="sortTable('lastName')">Last Name</th>
<th @click="sortTable('address')">Address</th>
<th>Phone number</th>
</tr>
# Search + filters + sort
searchVideos() {
let filtered = this.videos;
// search by keyword
if (this.filters.searchQuery) {
filtered = this.videos.filter(
v => v.title.toLowerCase().indexOf(this.filters.searchQuery) > -1
);
}
// filter by date range
if (this.filters.startDate && this.filters.endDate) {
filtered = filtered.filter(v => {
var time = new Date(v.created_at).getTime();
return (new Date(this.filters.startDate).getTime() < time && time < new Date(this.filters.endDate).getTime());
});
}
// filter by property value
if (this.filters.filterVal) {
if (this.filters.filterVal === 'female') {
filtered = filtered.filter(
v => v.gender === this.filters.filterVal
);
}
// sort by property
if (this.filters.sortValue === 'most_popular') {
filtered.sort(function(a, b) { return a.views - b.views; });
}
}
return filtered;
}
# async await
An async function returns a promise. When you want to call this function you prepend await, and the calling code will stop until the promise is resolved or rejected.
// example
const doSomethingAsync = () => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve('I did something'), 3000)
})
}
const doSomething = async () => {
console.log(await doSomethingAsync())
console.log('I did something again!')
}
doSomething()
// result:
// I did something!
// I did something again!
# async await with fetch in vuex
// example
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
data: null
},
mutations: {
setData: (state, payload) => {
state.resource = payload
}
},
actions: {
async getData({ commit }) {
let res = null
try {
res = await fetch(
'https://api.coindesk.com/v1/bpi/currentprice.json'
)
} catch (err) {
console.log('err: ', err)
return
}
// Handle success
console.log('waiting for data...');
const data = await res.json()
console.log('data: ', data)
commit('setData', data)
}
}
})
# import config file
// config.js
// example config file
var apiPort = 5566;
var currHost = window.location.protocol + '//' + window.location.hostname + ':' + apiPort + '/api/v1';
var url = window.location.host !== 'localhost:8080' ? 'http://PROD-URL/' : currHost;
export var cfg = {
version: "0.1.0",
api: {
endpoint: url
}
};
// main.js
import * as config from './config'
window._cfg = config.cfg
# Focus on a field
mounted() {
this.$refs.myInput.focus();
}
# Stuff that might get handy
- v-once - render the element and component only once
- v-if - conditionally render the element
- Difference between computed and methods
- watch - specify what property to listen for changes and then execute some code without returning values
- v-model modifiers
- .lazy - fire event when user lefts the field
- .number - force the value to be converted to a integer
- .trim - delete whitespace